Author: Julia Sun
The Dutch agency Wemos evaluated 15 international initiatives in response to the new coronavirus epidemic. What conclusions did it draw?
Total words1896About3minutes
In February 2022, the Dutch NGO Wemos launched a new website "covid19response.org". This website introduces15 countries promoting global distribution of COVID-19 medical productsinternational initiative(See the appendix at the end of the article for details), and evaluate the role these initiatives play in promoting an equitable and effective response to global infectious diseases.
Wemos evaluated fifteen initiatives based on five principles:
- sufficiency: Evaluate whether the initiative helps meet the global need for innovation in response to the COVID-19 pandemic.
- urgency: Assess the extent to which initiatives urgently increase global access to COVID-19 innovation outcomes.
- sustainability: Assess the initiative's ability to support global recovery from future public health emergencies.
- balance of power: Assess whether initiatives contribute to greater equality in high-income and lower-middle-income countries.
- Public interest comes first: Assess the extent to which initiatives prioritize public interests over commercial interests.

Different initiatives have different priorities
Among the fifteen initiatives, initiatives such as COVAX and the European Health Emergency Preparedness and Response Agency (HERA) focus on promoting the equitable distribution of COVID-19 medical products; initiatives such as the Multilateral Leaders Working Group support the local production of COVID-19 medical products in low- and middle-income countries; Initiatives such as TRIPS exemptions and mRNA centers support low- and middle-income countries in obtaining relevant technologies and independently conducting non-patented production. This article introduces the Wemos assessment using the three initiatives of the mRNA Center, COVAX and Regional Window as examples.
mRNA Vaccine Technology Transfer Center (mRNA)
In June 2021, the World Health Organization (WHO), the Medicines Patent Pool (MPP) and the South African consortium (Afrigen, Biovac and the South African Medical Research Council) took the lead in establishing an mRNA center in South Africa.The ultimate goal of the center is to establish long-term production capacity for COVID-19 mRNA vaccines in low- and middle-income countries and improve vaccine accessibility and self-sufficiency. The center plans to raise 92 million euros (approximately US$99.28 million) over five years, and has already raised half of the funds.
The establishment of the mRNA Center is of great significance to the world's more equal access to medical technologies such as mRNA vaccines. Its advantage is that the hub-and-spoke model is used in areas with insufficient production capacity.Localized production of mRNA vaccinesThis has created conditions for the mRNA Center to take advantage of existing production capacity and is expected to have a long-term impact on vaccine self-sufficiency in low- and middle-income countries.
Additionally, the mRNA Center is available forDeveloping mRNA vaccines for tuberculosis, HIV and other diseases, more economically sustainable. The challenge facing the mRNA center is that it requires a lot of funding to meet and expand demand in other countries and regions, and the implementation cycle is long, ranging from 24 to 36 months.
COVID-19 Vaccine Implementation Plan (COVAX)
In March 2020, COVAX was jointly launched by the Coalition for Epidemic Preparedness Innovations (CEPI), the Global Alliance for Vaccines and Immunization, and the World Health Organization (WHO).COVAX is a centralized procurement and distribution mechanism for COVID-19 vaccines that aims to provide vaccines to at least 20% of the population in 92 low- and middle-income countries. COVAX's procurement and distribution target by the end of 2021 has been adjusted from an initial 2 billion doses to 1.4 billion doses. On January 15, 2022, COVAX will be implemented1 billion vaccines deliveredmilestone.
The Access to Covid-19 Tools Accelerator (ACT-A), built on COVAX, aims to accelerate the development, production and equitable distribution of COVID-19 vaccines, medicines and diagnostics. ACT-A mobilizes $18.9 billion in government, corporate and philanthropic funding. As of October 2021, there is still a funding gap of US$14.2 billion.
COVAX hasTwo major advantages: First, as a short-term measure to enable rapid and fair distribution of vaccines; second, from proportional distribution to prioritizing countries with the lowest vaccine coverage.
COVAX also existschallenge: First, contracts between high-income countries and vaccine manufacturers squeeze out inventories, causing COVAX to be unable to achieve its procurement targets; second, donation targets for many high-income countries have not yet been achieved; third, low-income countries are still dependent on high-income countries and pharmaceutical companies.
Region window (RW)
The regional window launched by the International Development Association (IDA) in 2003 has been paying attention to the new crown epidemic since December 2021.The World Bank's International Development Association (IDA) provides concessional loans or grants to low-income countries. The regional window provides additional funding for regional solutions to development challenges in low-income countries. Regional window projects involve the participation of at least two eligible countries to encourage inter-country and regional cooperation. Funding may also be used to promote global public goods or reduce barriers to access to global public goods.
The area window hasTwo advantages. The first is to provide additional preferential loans or grants to countries to address population and health system vaccination challenges; the second is to support low-income countries in cooperating in COVID-19 vaccine procurement and enhance their market negotiation position.
The IDA area window also facestwo challenges. First, it does not involve sharing intellectual property and proprietary technology, and it is impossible to establish and utilize local production capabilities for medical products; second, preferential loans still need to be repaid, posing a burden to the limited health budgets of low-income countries, and the high prices of medical products such as vaccines make it even more difficult. It's adding insult to injury.
Developing countries call for fair distribution of vaccines and medicines
Promote fair distribution of medical innovation results
Countries around the world need access to innovative medical achievements such as vaccines and medicines to effectively prevent and treat current and future pandemics. However, access to vaccines and medicines varies widely across countries.
High-income countries have vaccinated their populations multiple times, while lower-income countries face severe vaccine shortages. This disparity results in economic and human losses that should not occur. therefore,It is crucial to establish a global medical innovation system that serves the global public interest rather than purely commercial or national interests..
Increase self-sufficiency in COVID-19 vaccines and medicines
Only by increasing global innovation in COVID-19 vaccines and drugs and promoting self-sufficiency in low- and middle-income countries can we respond to the epidemic more equitably and effectively.. This would break reliance on high-income countries and a handful of pharmaceutical companies, incentivize more locally tailored solutions, push vaccine and drug prices downwards, and invest in local production capacity in low- and middle-income countries to boost public health emergencies. of resilience.
Wemos calls on governments to support initiatives such as the COVID-19 Technology Access Pool (C-TAP) to promote the sharing of production knowledge and technology, and to support TRIPS exemption proposals to allow pharmaceutical companies other than patent holders to produce COVID-19 innovative products.
Wemos believes that the South African mRNA Center has made great progress in the research and development of mRNA vaccines.This model seeks to produce and distribute vaccines locally and strengthen local capacity building, providing a structural solution for equitable vaccine distribution, with an impact that will go far beyond the COVID-19 epidemic itself.
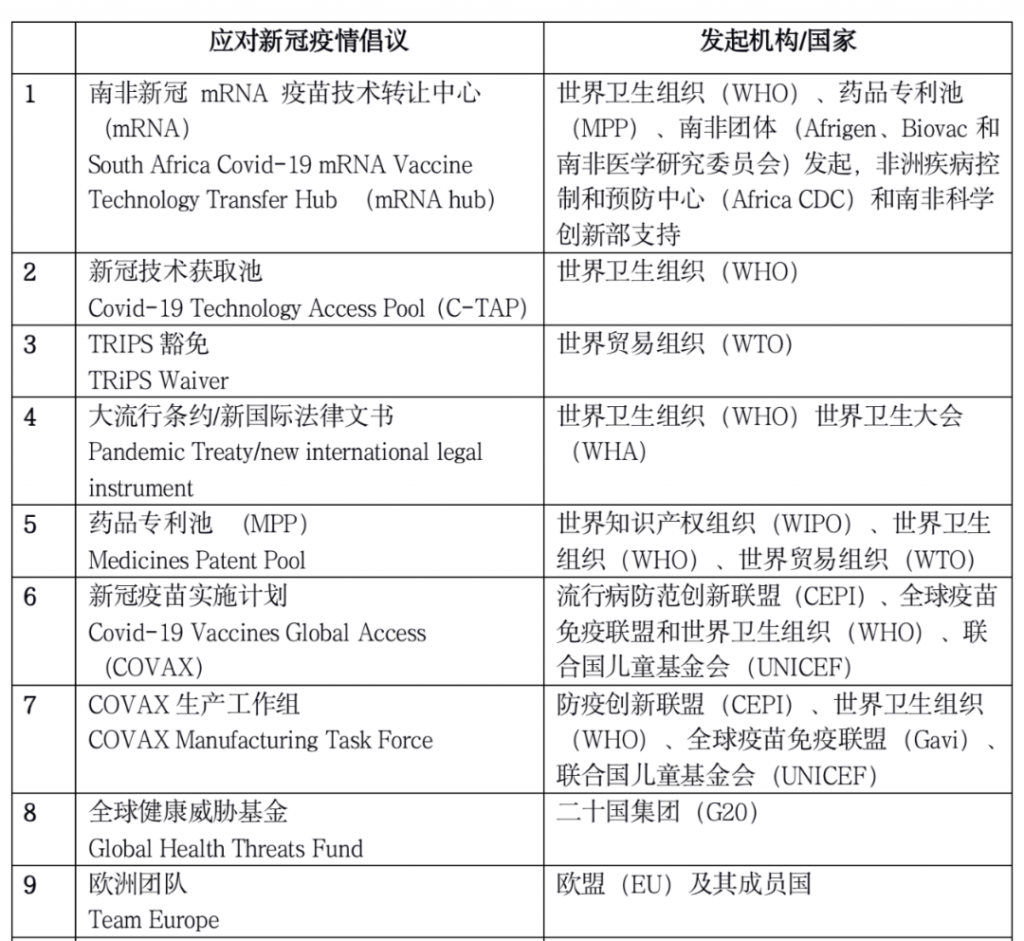
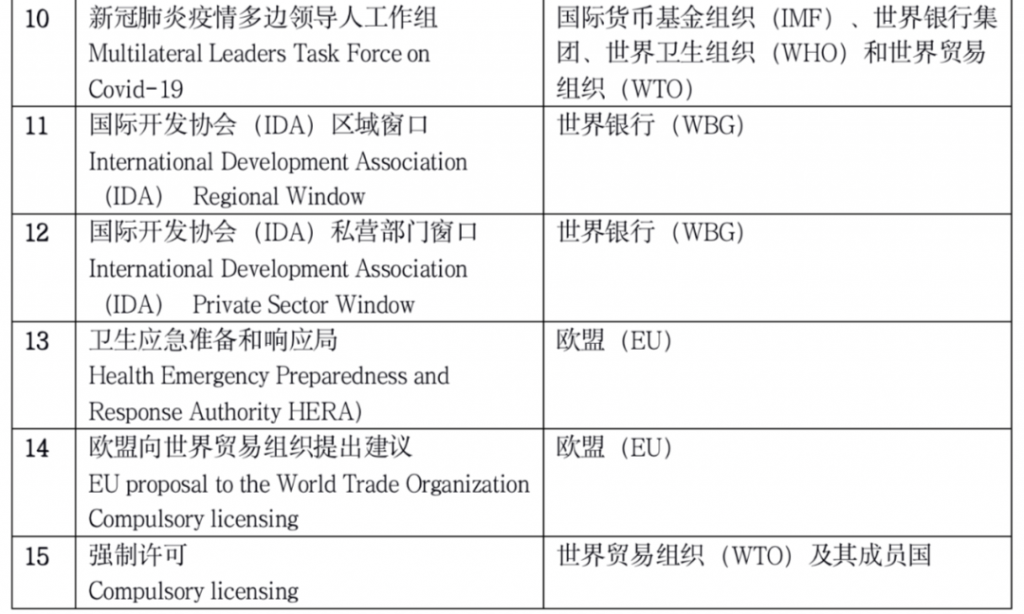
- Appendix: 15 international initiatives to respond to the COVID-19 epidemic
All rights reserved, please indicate the source when citing.
References
New website provides overview and review of initiatives for access to medical products against Covid-19
https://www.who.int/zh/initiatives/act-accelerator/covaxhttps://covid19response.org/
Past review
- Constricted Aid Budgets and Dwindling Support: UK NGOs' Struggle to Forge Ahead
- New Trends of Global Donor Countries in 2021: Development Cooperation in the Era of Pandemic (Europe)
- Recapping International Development in 2021
- International Humanitarian Aid: Where? Who? How?
- Is COVID-19 the Final Straw for Triggering Debt Crisis in Developing Countries?
The pictures in this article come from the Internet
